How to install Kubernetes with microk8s and deploy apps on Debian/Mint/Ubuntu Linux
Kubernetes Easy Beginners Tutorial/Architecture Guide
Kubernetes is known as container orchestration and we should start at explaining the container part of it.
A Container is what runs the actual application and based on an Image, and are more comparable to something like an LXC Container, Virtuozzo/OpenVZ using the Linux Kernel Namespaces feature. Containers run these images as independent, isolated operating environments under the OS's existing kernel. Unlike full virtualization which emulates a real computer, images run under the existing OS kernel and do not have their own virtual hardware, which makes them perform and deploy faster.
An Image is like a pre-built template that has everything we need to run the application eg. nginx, Apache, MySQL and almost anything can be turned into a purpose built application inside an image file.
Multiple Containers run within Pods (although most often 1 container will run inside a pod), and Multiple Pods can run on Nodes, and there can be Multiple Nodes in the Cluster, which is the general/basic hierarchy of Kubernetes.
Pods are basically just a grouping of Containers which are generally related or may need to have tighter coupling of storage and networking (many pods still have just 1 container).
Nodes can be anything that runs the kubernetes services, and would most commonly be some sort of VM or even a physical server. VMs are recommended for Kubernetes as it is more easy to fix problems or troubleshoot and make changes/upgrades compared to bare metal dedicated servers.
Prerequisites
RAM: 4G minimum (8G and much higher recommended for any workloads)
HDD: 20G minium
Hostname: No capitals and no underscores
OS: Latest / newer Linux distro
This guide was written for Ubuntu 20/Mint 20 at the time.
At the time of update the latest microk8s classic is 1.26.3 and this worked fine on Ubuntu 22 and Debian 11.
https://microk8s.io/docs/troubleshooting
Step 1 - Install snapd and microk8s
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl-linux/
Note that Linux Mint disables snap, read this post to fix snapd install missing in Linux Mint.
snapd installation
sudo apt install snapd
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following NEW packages will be installed:
kubernetes
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 123 not upgraded.
Need to get 3,340 B of archives.
After this operation, 19.5 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 kubernetes all 1.0 [3,340 B]
Fetched 3,340 B in 0s (9,475 B/s)
Selecting previously unselected package kubernetes.
(Reading database ... 378576 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../kubernetes_1.0_all.deb ...
Unpacking kubernetes (1.0) ...
Setting up kubernetes (1.0) ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) ...
microk8s installation
#the channel version is very important. At the original time of writing the default channel was 1.20 and today it is 1.26.3, there are often big changes in each channel/version that may cause things to break. For example at the time of writing the default channel of 1.20 worked fine on Ubuntu 20/Mint 20, but today version 1.26.3 which is the default, is broken (although it works fine on Debian 11).
So you should specify a certain channel and be aware of which one you are working on to avoid surprises, changes and incompatibilities in the future.
snap install microk8s --classic --channel=1.19
#I recommend you set this alias so you can call kubectl without using microk8s.kubectl
alias kubectl=microk8s.kubectl

Create our first app deployment using nginx
microk8s.kubectl create deployment nginx --image nginx
deployment.apps/nginx created
enable/expose it so it can start working
microk8s.kubectl expose deployment nginx --port 8000 --target-port 8000 --selector app=nginx --type ClusterIP --name rtttest
service/rtttest exposed
View all running services:
microk8s.kubectl get all
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-6799fc88d8-sm5gd 1/1 Running 0 3m43s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.152.183.1
service/areebtest ClusterIP 10.152.183.191
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 1/1 1 1 3m43s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/nginx-6799fc88d8 1 1 1 3m43s
Enable Dashboard
Enabling DNS
Applying manifest
serviceaccount/coredns created
configmap/coredns created
Warning: spec.template.metadata.annotations[scheduler.alpha.kubernetes.io/critical-pod]: non-functional in v1.16+; use the "priorityClassName" field instead
deployment.apps/coredns created
service/kube-dns created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/coredns created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/coredns created
Restarting kubelet
DNS is enabled
Enabling Kubernetes Dashboard
Enabling Metrics-Server
serviceaccount/metrics-server created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:aggregated-metrics-reader created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server-auth-reader created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server:system:auth-delegator created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
service/metrics-server created
deployment.apps/metrics-server created
apiservice.apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/microk8s-admin created
Metrics-Server is enabled
Applying manifest
serviceaccount/kubernetes-dashboard created
service/kubernetes-dashboard created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-certs created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-csrf created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder created
configmap/kubernetes-dashboard-settings created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
Warning: spec.template.spec.nodeSelector[beta.kubernetes.io/os]: deprecated since v1.14; use "kubernetes.io/os" instead
deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard created
service/dashboard-metrics-scraper created
deployment.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper created
token=$(microk8s kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep default-token | cut -d " " -f1)
microk8s kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $token
In an RBAC enabled setup (microk8s enable RBAC) you need to create a user with restricted
permissions as shown in:
https://github.com/kubernetes/dashboard/blob/master/docs/user/access-control/creating-sample-user.md
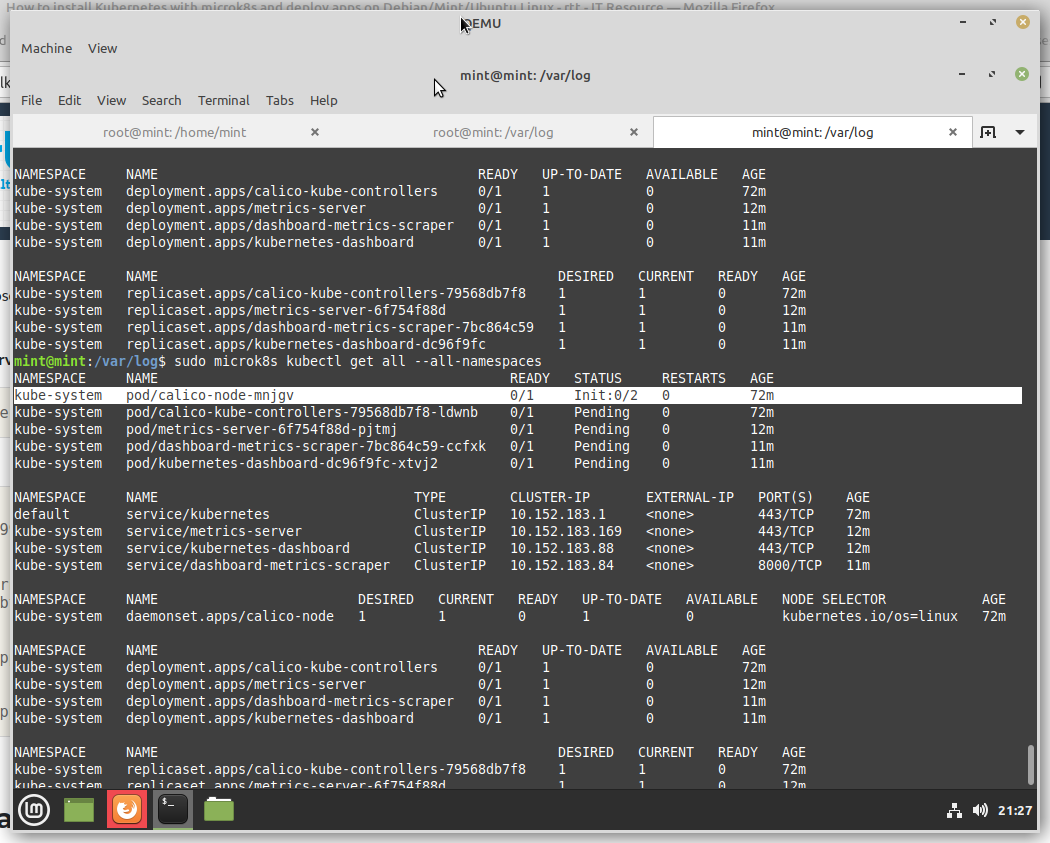
microk8s.kubectl get all --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
default pod/nginx-6799fc88d8-sm5gd 1/1 Running 1 (134m ago) 147m
kube-system pod/coredns-7f9c69c78c-jhhkq 1/1 Running 0 2m25s
kube-system pod/calico-node-2jnsp 1/1 Running 1 (134m ago) 169m
kube-system pod/calico-kube-controllers-58d7965c58-qpw8j 1/1 Running 1 (134m ago) 169m
kube-system pod/dashboard-metrics-scraper-58d4977855-7dnzm 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 13s
kube-system pod/kubernetes-dashboard-59699458b-7t52l 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 13s
kube-system pod/metrics-server-85df567dd8-7rfsm 0/1 Running 0 13s
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.152.183.1
default service/areebtest ClusterIP 10.152.183.191
kube-system service/kube-dns ClusterIP 10.152.183.10
kube-system service/metrics-server ClusterIP 10.152.183.124
kube-system service/kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.152.183.109
kube-system service/dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.152.183.24
NAMESPACE NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
kube-system daemonset.apps/calico-node 1 1 1 1 1 kubernetes.io/os=linux 169m
NAMESPACE NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
kube-system deployment.apps/calico-kube-controllers 1/1 1 1 169m
default deployment.apps/nginx 1/1 1 1 147m
kube-system deployment.apps/coredns 1/1 1 1 2m26s
kube-system deployment.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper 0/1 1 0 77s
kube-system deployment.apps/metrics-server 0/1 1 0 97s
kube-system deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard 0/1 1 0 77s
NAMESPACE NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
kube-system replicaset.apps/calico-kube-controllers-58d7965c58 1 1 1 169m
default replicaset.apps/nginx-6799fc88d8 1 1 1 147m
kube-system replicaset.apps/coredns-7f9c69c78c 1 1 1 2m26s
kube-system replicaset.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper-58d4977855 1 1 0 13s
kube-system replicaset.apps/metrics-server-85df567dd8 1 1 0 13s
kube-system replicaset.apps/kubernetes-dashboard-59699458b 1 1 0 13s
How to Expose the Dashboard
microk8s.kubectl expose service kubernetes-dashboard -n kube-system --port 8000 --type=NodePort --name kubserv
service/kubserv exposed
This is an excellent intro to namespaces, as you will notice the dashboard belongs to the namespace "kube-system" so we have to use "-n" for namespace and specify kube-system or it will not work (without -n it defaults to the "default" namespace). As when we exposed nginx previously, it was running in the "default" namespace.
kube-system service/kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.152.183.130
default service/areebtest ClusterIP 10.152.183.157
We can also delete the "kubserv" exposed service:
microk8s.kubectl delete service -n kube-system kubserv
service "kubserv" deleted
Troubleshooting
Pod not starting errors?
Say you check your pods and find this error:
kubectl get pods
wordpress-mysql-66dcbc8d8c-6llhx 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 4 (27s ago) 3m11s
Check the pod log:
microk8s.kubectl logs wordpress-mysql-66dcbc8d8c-6llhx
Fatal glibc error: CPU does not support x86-64-v2
This is sometimes caused by a plain KVM CPU with out -v2 flags or a CPU that doesn't support them.
The practical solution is to downgrade to an older image of this mysql to an older version (eg. this happened on Version 8.)
==========================
If you get these sorts of errors right after installing, you have bad or incompatible version of microk8s and should get an older version.
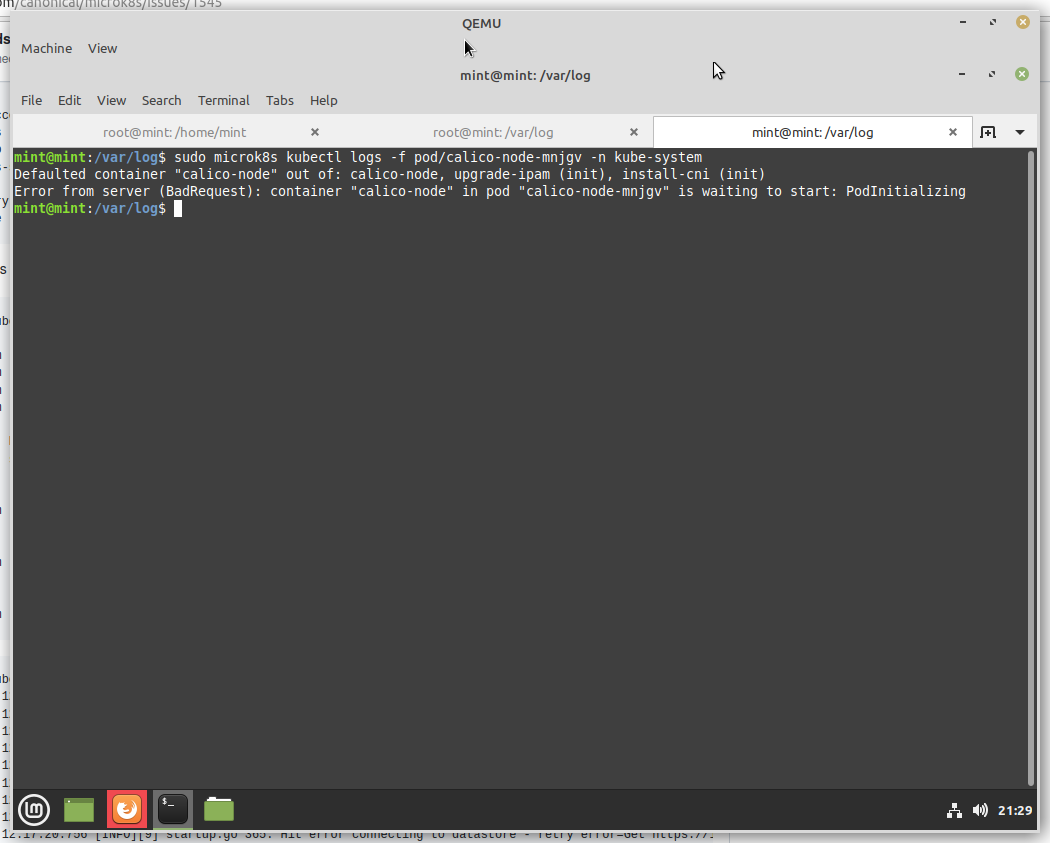
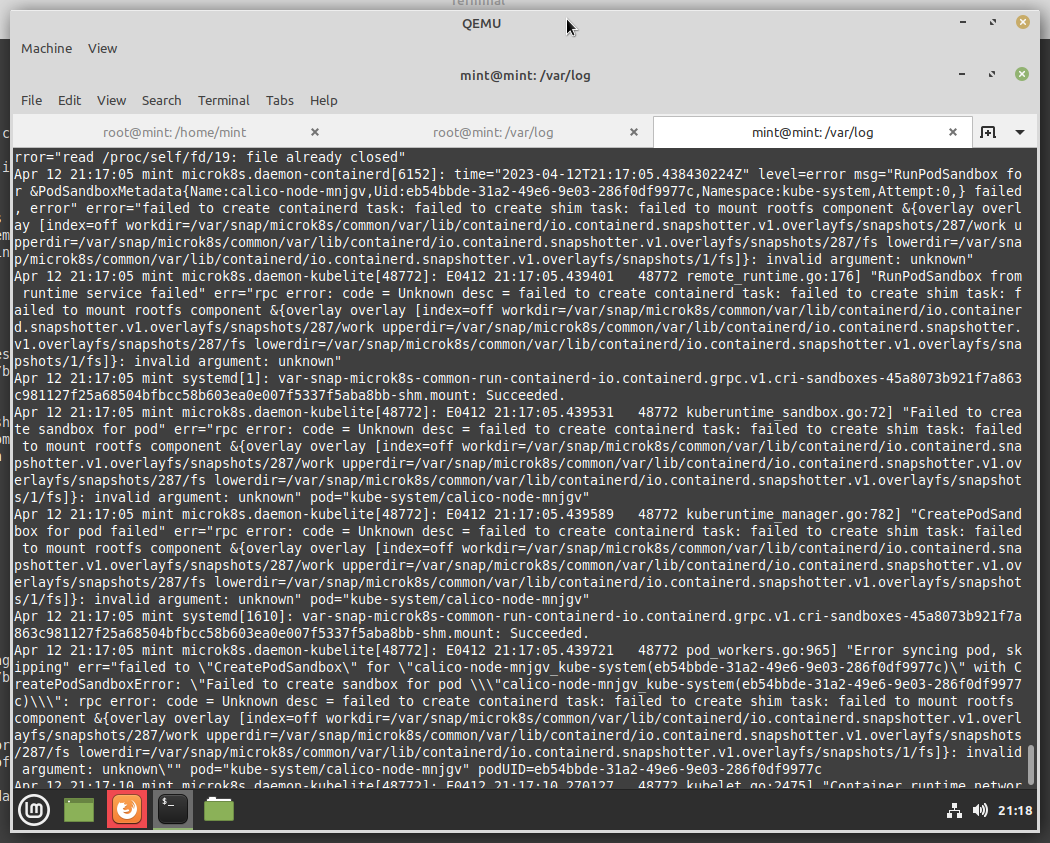
Kubernetes microk8s / calico won't start, stuck on initializing after the install
Let's Extend To an HA Kubernetes Cluster:
On the first node from above that you already created, run this command:
microk8s add-node
From the node you wish to join to this cluster, run the following:
microk8s join 10.10.10.7:25000/ad78ec7249c39d0870d77ea0199fe814/9d2708e1aae1
If the node you are adding is not reachable through the default interface you can use one of the following:
microk8s join 10.10.10.7:25000/ad78ec7249c39d0870d77ea0199fe814/9d2708e1aae1
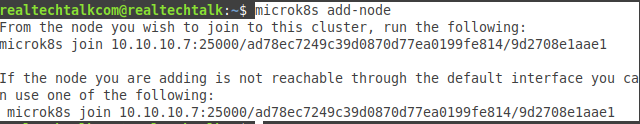
On the other nodes, use the join statement from above: microk8s join 10.10.10.7:25000/ad78ec7249c39d0870d77ea0199fe814/9d2708e1aae1
microk8s cluster invalid token (500)
If you are sure everything was done right and the issue mentioned below is not your problem, just run "microk8s add-node" again to generate a new token.
Be sure that you have connectivity to the master node in the join statement, that no firewall is blocking the connection, and that the join statement is copied and pasted correctly without any extra whitespace in the middle or typos.
Resources:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/
Old Broken stuff
kubernetes install
Choose 1 for microk8s:
Tags:
install, kubernetes, debian, mint, ubuntu, linuxhttps, io, docs, tasks, kubectl, linux, https, microk, sudo, apt, snapd, lists, dependency, packages, installed, upgraded, newly, archives, kb, additional, disk, http, archive, focal, amd, fetched, selecting, previously, unselected, database, directories, currently, preparing, unpack, kubernetes_, _all, deb, unpacking, processing, triggers, db, enable, ips, ufw, firewall, apps, cni, default, routed, app, deployment, nginx, images, selector, clusterip, rtttest, restarts, pod, fc, sm, gd, cluster, ip, external, tcp, areebtest, desired, replicaset, dashboard, dns, enabling, applying, manifest, serviceaccount, coredns, configmap, spec, template, metadata, annotations, scheduler, alpha, functional, quot, priorityclassname, kube, clusterrole, rbac, authorization, clusterrolebinding, restarting, kubelet, enabled, metrics, server, aggregated, reader, rolebinding, auth, delegator, apiservice, apiregistration, beta, admin, certs, csrf, holder, settings, nodeselector, os, deprecated, scraper, token, retrieved, grep, user, restricted, permissions, github, blob, creating, md, namespaces, namespace, jhhkq, calico, node, jnsp, controllers, qpw, dnzm, containercreating, df, dd, rfsm, udp, daemonset, echo, nodeport, nic, microbot, vm, publicly,
